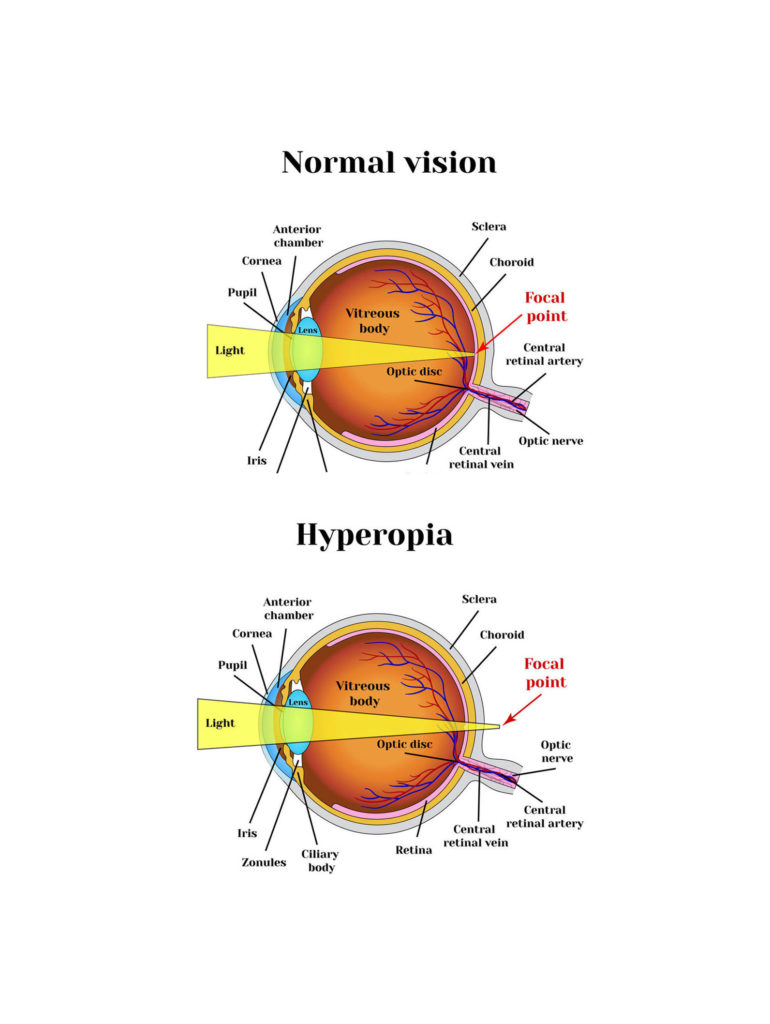
Far-sightedness, also known as hyperopia, is a condition of the eye in which light is focused behind, instead of on, the retina. This results in close objects appearing blurry, while far objects may appear normal. As the condition worsens, objects at all distances may be blurry. Other symptoms may include headaches and eye strain. People may also experience accommodative dysfunction, binocular dysfunction, amblyopia, and strabismus.
The cause is an imperfection of the eyes. Often it occurs when the eyeball is too short, or the lens or cornea is misshapen. Risk factors include a family history of the condition, diabetes, certain medications, and tumors around the eye. It is a type of refractive error. Diagnosis is based on an eye exam.
Management can occur with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery. Glasses are easiest while contact lenses can provide a wider field of vision. Surgery works by changing the shape of the cornea. Far-sightedness primarily affects young children, with rates of 8% at 6 years and 1% at 15 years. It then becomes more common again after the age of 40, affecting about half of people.
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms of far-sightedness are blurry vision, headaches, and eye strain. The common symptom is eye strain. Difficulty seeing with both eyes (binocular vision) may occur, as well as difficulty with depth perception.
Complications
Far-sightedness can have rare complications such as strabismus and amblyopia. At a young age, severe far-sightedness can cause the child to have double vision as a result of "over-focusing".

Causes
Human eye cross-section
As hyperopia is the result of the visual image being focused behind the retina, it has two main causes:
Low converging power of eye lens because of weak action of ciliary muscles
Abnormal shape of the cornea
Far-sightedness is often present from birth, but children have a very flexible eye lens, which helps to compensate. In rare instances hyperopia can be due to diabetes, and problems with the blood vessels in the retina.
Diagnosis
Retina section
A diagnosis of far-sightedness can be made via a slit lamp test which examines the cornea, conjunctiva, and iris.
In severe cases of hyperopia from birth, the brain has difficulty in merging the images that each individual eye sees. This is because the images the brain receives from each eye are always blurred. A child with severe hyperopia can never see objects in detail. If the brain never learns to see objects in detail, then there is a high chance of one eye becoming dominant. The result is that the brain will block the impulses of the non-dominant eye. In contrast, the child with myopia can see objects close to the eye in detail and does learn at an early age to see detail in objects.
Treatment
Corrective lenses
The simplest form of treatment for far-sightedness is the use of corrective lenses, eyeglasses or contact lenses. Eyeglasses used to correct far-sightedness have convex lenses.
Surgery
There are also surgical treatments for far-sightedness:
Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK)
Removal of a minimal amount of the corneal surface
Laser assisted in situ keratomileusis (LASIK)
Laser eye surgery to reshape the cornea, so that glasses or contact lenses are no longer needed.
Refractive lens exchange (RLE)
A variation of cataract surgery where the natural crystalline lens is replaced with an artificial intraocular lens; the difference is the existence of abnormal ocular anatomy which causes a high refractive error.
Laser epithelial keratomileusis (LASEK)
Resembles PRK, but uses alcohol to loosen the corneal surface
